Type I diabetes is unfortunately a very common disease. More than 9 million people currently have type I diabetes, and figures keep going up.
Type 1 diabetes develops when the immune system targets insulin-produing beta cells in the pancreas. This process disrupts glucose regulation and requires lifelong insulin management. While current therapies focus on controlling blood sugar, stem cell research examines whether damaged pancreatic function can be supported or partially restored.
Here, we review how scientists study beta cell loss, why stem cells draw attention, and where evidence remains limited.
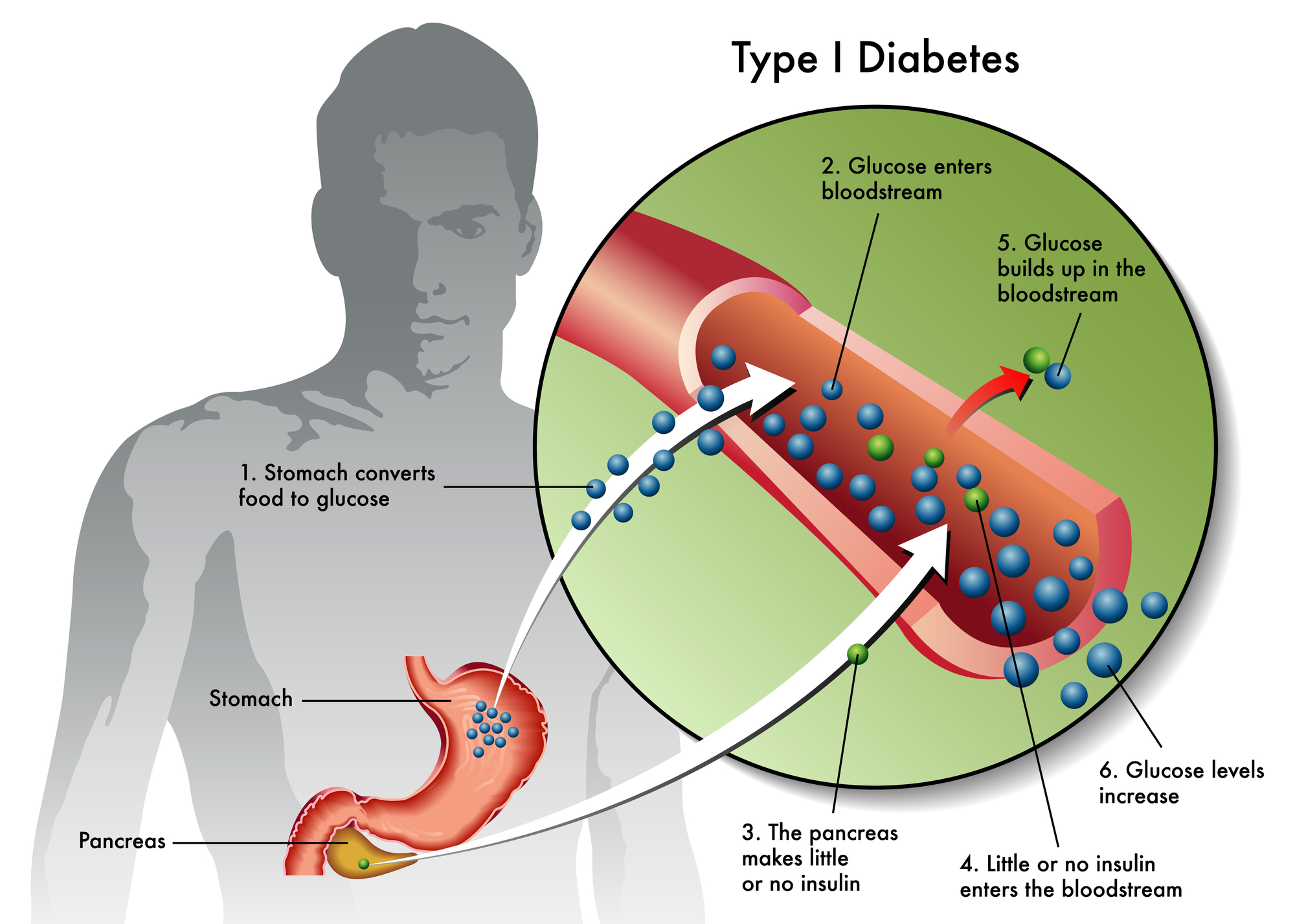
In Type I diabetes, immune cells mistakenly attack pancreatic beta cells. These cells normally sense blood glucose and release insulin. As beta cell mass declines, insulin production falls.
Most people receive a diagnosis after significant beta-cell loss has already occurred. At that stage, the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Even with careful management, glucose levels often fluctuate.
Researchers study beta cell regeneration because restoring even partial insulin secretion could improve glucose stability. This goal remains complex because immune activity often continues after diagnosis.
Scientists link Type 1 diabetes to autoimmune signaling rather than metabolic overload. Genetic susceptibility interacts with environmental triggers that remain under investigation.
Once activated, immune cells recognize beta cells as foreign. They release inflammatory signals that damage pancreatic tissue. Over time, this process reduces insulin capacity.
Stem cell research examines how immune signaling and cellular repair interact. Without immune regulation, regenerated cells may face the same destruction.
Beta cell regeneration refers to restoring functional insulin-producing cells. Researchers explore whether stem cells can support this process directly or indirectly.
Some studies examine whether stem cells can differentiate into insulin-secreting cells under laboratory conditions. Others focus on how stem cells influence inflammation and immune balance.
Rather than acting as simple replacements, stem cells appear to interact with surrounding tissues. These interactions shape cellular signaling and local immune responses.
Islet cells include beta cells and other hormone-secreting pancreatic cells. Islet cell transplantation transfers healthy islet clusters into individuals with severe diabetes.
Research shows that transplanted islets can restore insulin production temporarily. However, immune rejection remains a major barrier. Most recipients require long-term immune suppression.
Islet cell transplantation informs stem cell research by clarifying how many functional cells are required. It also shows how immune responses limit durability.
Scientists use these insights to guide laboratory studies on stem-derived beta cells.
Researchers investigate several stem cell types in controlled laboratory environments. These include embryonic stem cells and adult progenitor cells.
In vitro studies examine whether stem cells can mature into insulin-responsive cells. Some experiments report glucose-responsive insulin secretion under specific conditions.
However, laboratory success does not always translate to stable function in living systems. Cells must survive immune exposure and integrate into pancreatic signaling.
Animal models help researchers observe how stem-derived cells behave over time. Results vary across studies and species.
Regenerative medicine focuses on restoring tissue balance rather than replacing organs. In Type I diabetes research, this approach includes immune modulation and cellular signaling support.
Stem cells release signaling molecules that influence inflammation and immune activity. These signals may help protect remaining beta cells.
Some research suggests that early intervention could preserve residual insulin production. Later stages appear more challenging due to extensive cell loss.
Differences in study design influence outcomes. These differences include cell sources, laboratory conditions, and immune status.
Timing also matters. Early disease stages differ biologically from advanced disease. Age, genetics, and metabolic health further affect results.
No standardized protocol exists across studies. This variation makes comparisons difficult and conclusions cautious. In addition, large-scale human trials remain limited.
Current research does not support a full restoration of pancreatic function. Some studies suggest partial insulin support under specific conditions.
Islet cell transplantation demonstrates proof of concept but faces immune challenges. Stem cell-derived approaches seek to address these barriers.
Long-term durability remains uncertain. Researchers continue to evaluate whether regenerated cells can persist without immune suppression.
Inflammation shapes beta cell loss and regeneration. Chronic immune activation disrupts pancreatic signaling.
Stem cell research explores whether anti-inflammatory signaling can protect vulnerable cells. This approach may complement regeneration efforts.
Reducing inflammatory stress could help preserve remaining beta cells. This concept remains under active investigation.
Systemic inflammation also affects glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Whole-body health influences pancreatic outcomes.
Metabolic health affects immune regulation and cellular repair capacity. Factors like sleep, stress, and nutrient balance matter.
Researchers observe better outcomes in models with lower inflammatory burden. These findings highlight the role of lifestyle and systemic health.
Stem cell research does not occur in isolation. It intersects with broader metabolic and immune pathways, and understanding these interactions remains a central research goal.
Scientists continue refining differentiation methods and immune protection strategies. Some studies combine stem cell approaches with immune modulation.
Others examine how to shield regenerated cells from immune recognition. Encapsulation and signaling control receive attention.
Progress remains gradual and iterative. Each study contributes data rather than definitive solutions. Regenerative medicine continues to evolve alongside immunology and endocrinology.
Type 1 diabetes reflects complex immune and cellular processes. Stem cell research examines how beta cell regeneration and immune balance may interact over time.
Cellebration Wellness focuses on education grounded in current research and regenerative approaches inspired by the latest advances in stem cell research.
To learn more or schedule a general wellness consultation, don't hesitate to contact Cellebration Wellness at (858) 258-5090 today.
